
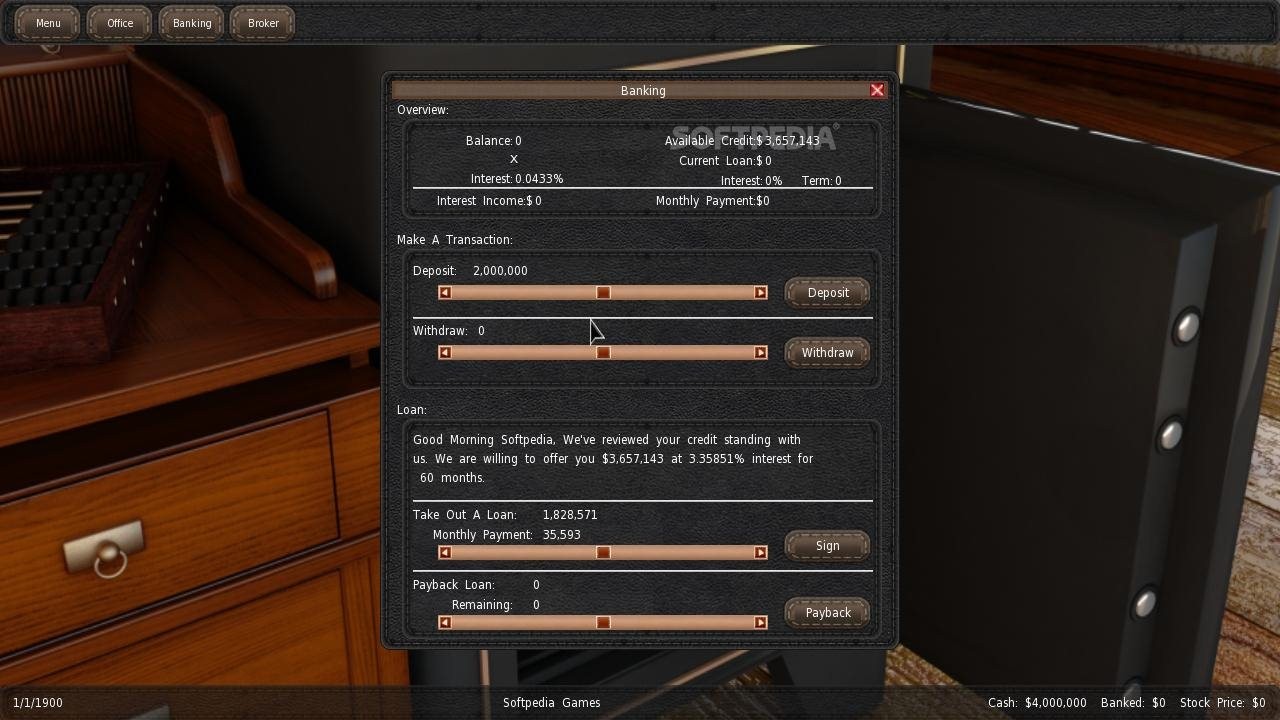
This defines the width multiplier for the engine layout. The higher this is, the longer it will take to develop the engine. This is how much of an effect on development the engine layout has on the engine. The higher this is, the harder it will be to manufacture, thus reducing the number of units you can produce per turn. This is how difficult it is to manufacture the engine layout. Higher values here will increase the engine design difficulty This is how difficult it is to design the engine layout. The higher this number is, the heavier the engine will be.

This is how much effect the engine layout has on the weight of the engine. The higher this number the more reliably this design is. This is the engine layout's effect on engine reliability. This is how much the engine layout effects the design costs, the higher this number is the more expensive it will be to design. Higher this number is the more expensive the engine will be. This effects the costs of the engine based on the layout selection. This value will automatically decrease over time after the “start” year has been hit. This is the minimum amount of Chassis Design skills points needed to unlock the drivetrain. +Increases Chassis' Supported Engine Length Higher numbers here will means you'll be able to use bigger engines. This effects the maximum supported engine length of the chassis. +Increases Chassis' Supported Engine Width This effects the maximum supported engine width of the chassis. The higher the values, the more it costs. Higher the value the harder it is to make.

This is how difficult the drivetrain is to manufacturer. This variable is for the difficulty in design with this drivetrain. This variable is for the weight of the drivetrain layout. Represents how durable the drivetrain layout is. Higher values here typically means more performance oriented chassis systems. This is the drivetrains's effects vehicle performance. This is the drivetrains's effects on drivability, handling, and roadhold of the chassis. The higher this rating is, the less skills one requires to drive this vehicle in poor conditions such as wet roads and at high speeds. This is the drivetrain's effect on how 'easy' the vehicle is to drive.
This is how well the suspension system handles stress. The higher this value the better the suspension is at high speed handling. This is the effect on performance for the suspension.
#Gearcity wikia driver#
The more comfortable the suspension, the less likely the driver will notice problems in the road. This shows how well the suspension system handles bumps, holes, and other road obstacles. Higher the value the better it is at braking. This is the suspension's effect on stopping the vehicle. Higher values here typically means more performance oriented suspension systems. This is the suspension's effects on drivability, handling, and roadhold of the chassis. This is the base percentage of how likely the AI is to use this item if no AI components Popularity file is present. This is the minimum amount of Chassis Design skills points needed to unlock the frame. Units per factory line, -More advance factory needed to not have per line penalties. This is how difficult the frame is to manufacturer. This variable is for the difficulty in design with this frame. Weight, -Performance, -Fuel Economy, -Driveability, -LateralG, -Braking, -Acceleration, -Top Speed Manufacturing Requirements, -Weight, +Strength This variable is for the weight of the frame. Some designs may require more weight to implement than others. This is how long the frame design typically lasts and how much stress it can handle over time. Represents the chassis safety design, such as crumple zones design, and how well the chassis absorbs and distributes impacts on the vehicle. +LateralG, +Braking, +Safety (Due to LateralG and Braking), +Performance, +Driveability Represents how strong the frame is in its ability to handle stresses and weight.Ĭonveys the chassis handling abilities, it's roadhold, and how well it handles torsional stresses to maximize traction.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
